- 1: Discourage Memorization: Start with Multiplication as Repeated Addition.
- 2: Show the Magic of Zero (Zero Property of Multiplication)
- 3: Teach the Property of One (Identity Property of Multiplication)
- 4: Start with Easy Numbers to Introduce Multiplication Tables
- 5: Practice, Practice, and Practice! Introduce More Multiplication Tables and Multiplication Facts!
- 6: Teach the 3 Important Properties of Multiplication: Commutative, Associative, and Distributive
- 7:. Show the Relationship between Tables and Discuss Patterns
- 8: Break Down the Number to Simplify the Problem
- 9: Tell Them the the Relationship Between Multiplication and Division
- 10: Use Visuals: Introduce the Area Model Method for 2 × 2 Multiplication.
- 11: Standard Algorithm for Multiplication
Are you a primary school math teacher trying to figure out how to teach multiplication to your students? Well, then, you have landed on the right post. We will discuss easy and fun ways to teach multiplication to students.
Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun.
You see real learning outcomes.
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free
Math may not always top students’ favorites list, but it lays the foundation for countless everyday life skills. Be it telling time or counting money, everything is math. Among the four core elements of math (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division), multiplication is the most crucial one. It sets the ground for many advanced mathematical concepts like algebra and calculus.
As a primary school math teacher, you are responsible for teaching multiplication and making it fun and exciting for your class. If you get your students interested in math now, you can give them several prosperous academic years ahead. Don’t stress, though, for we are here to help! Let’s explore some engaging and easy ways to teach multiplication to kids.
Related Reading: Best Multiplication Tricks for Math Students
How to Teach Multiplication in 11 Easy Steps
Multiplication is a fundamental math skill that opens the door to understanding advanced concepts. While the process often starts with memorizing tables, learning multiplication doesn’t have to be boring or monotonous. Instead of relying solely on rote learning, there are some creative strategies that teachers and parents can use to simplify learning multiplication for kids. Here are the best strategies to teach multiplication to students:
Step 1: Discourage Memorization: Start with Multiplication as Repeated Addition.
Students often struggle with memorization. They find it challenging to learn and implement all the tables in a problem. Some children get so scared of table memorization that they fear doing math.
To prevent this, the best strategy is to show your class the relationship between multiplication and addition. This strategy can also help students understand the multiplication concept, which is repeated addition. Before kids dive into multiplication tables, build a foundational understanding of what multiplication means conceptually.
Use relatable examples to show your class how multiplication is based on addition. As your class would have already learned addition in previous lessons, if not, they can easily learn addition by playing free online addition fact games. This will make them more comfortable with multiplication in less time.
You can write these equations on your blackboard to help your struggling students with visuals:
3 × 3 is the same as 3 + 3 + 3 (3 equal groups of 3)
Or
4 × 2 is the same as 4 + 4 (2 equal groups of 4)
The best way to reinforce multiplication as repeated addition is through concrete models like multiplication arrays (a way to organize objects into equal groups in rows and columns), skip counting, and a number line.
- Multiplication Using Arrays: For instance, teach kids how to form and look at multiplication arrays as equal groups.
4 rows and 3 columns = 4 equal groups of 3 = 4 × 3 = 12
Ways to Teach Multiplication Using Arrays:
i) Use small objects like coins or buttons to create arrays (e.g., 3 rows of 4) and count the total.
ii) Draw arrays on graph paper and ask kids to identify the multiplication expression.
iii) Games on Multiplication with Arrays: In these virtual math games, kids will practice everything from understanding the rows and columns in an array to creating arrays using real-world objects to represent the given multiplication sentences.
Play and master multiplication arrays!
- Multiplication by Skip Counting: Skip counting involves counting forward by a specific number (e.g., 2, 4, 6, 8 for counting by 2s). It helps students recognize multiplication as repeated addition.
Example: To find 5 × 3, students count: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15.
Ways to Teach Multiplication Using Skip Counting:
i) Skip count using steps (e.g., count by 3s up to 30) while clapping or hopping for each number.
ii) Teach students to skip counting with their fingers or use manipulatives like counters or tally marks.
iii) Skip Counting Games: Kids will learn the basics of multiplication through activities like counting by 2s, 5s, and 10s on a hundreds chart, counting objects in pairs, and figuring out the next number in a skip counting sequence to tackle fun challenges.
Ready to practice skip counting in a fun way?
Begin here
- Multiplication on a Number Line: When understanding multiplication on a number line, 3 × 4 means taking 3 jumps starting from 0, where the size of each jump is 4.
Ways to Teach Multiplication Using a Number Line:
i) Create a number line on the floor with tape and have your child take equal jumps.
ii) Fun Games on Multiplication on a Number Line: Practice representing and identifying multiplication facts on a number line.
Let’s learn multiplication on a number line!
Begin here
iii) Use a toy car or figure to “jump” along the number line for each multiplication step.
Step 2: Show the Magic of Zero (Zero Property of Multiplication)
Before getting into complex numbers, you should show your students how multiplication by zero works in mathematics. Emphasize that adding 0 to any number always results in the same number, but after multiplying any number by 0 the product is always 0.
Here, you can use this visual example:
n + 0 = n
But . . .
n × 0 = 0
This can be understood through repeated addition. For example, 3 x 0 means adding 0 three times: 0 + 0 + 0, which equals 0.
Ways to Teach the Zero Property of Multiplication:
i) Use a concrete example like 5 × 0 to explore the concept. Have your child create 5 groups with 0 objects in each and observe there’s nothing in total. Then, ask if it makes sense to form 0 groups with 5 objects, reinforcing that the total is always 0.
ii) Practice Worksheets: In these worksheets, kids will use their understanding of the property to solve fun problems like filling in missing numbers to complete the multiplication sentences.
Let’s multiply by 0!
Begin here
Teaching the zero property of multiplication alongside the identity property can help students understand both concepts more deeply. By comparing and contrasting these properties, students can see how they relate to each other.
Step 3: Teach the Property of One (Identity Property of Multiplication)
Like zero, the number one is also easy to multiply. Any number that multiplies with one retains its value:
n × 1 = n
Ways to Teach the Identity Property of Multiplication:
i) Worksheets for Independent Practice: In these worksheets, kids will solve mixed problems on multiplication by 1 and 0 to help kids avoid confusion. Also, they keep kids engaged through a variety of problem types.
Master the identity property of multiplication!
Begin here
ii) Discuss an example like 5 × 1. Ask your child to form 5 groups where each group has only one object. Count the total number of objects.
Step 4: Start with Easy Numbers to Introduce Multiplication Tables
To teach times tables, start with easy numbers that students can remember faster by identifying patterns.
For example, after teaching the number zero and the property of one, you can show your class the tables of 10 and 11. They are great starting points for learning multiplication because they often follow simple patterns. The 10 times table involves adding a zero to the number, while the 11 times table has a repeating digit pattern.
Make it fun! Reinforce times tables of 10 and 11 with these engaging and colorful worksheets where kids will solve wheel puzzles, horizontal and column problems, maze challenges, and more! Perfect for creating task cards for home practice!
Practice multiplication tables of 10 and 11 in fun ways!
Begin here
Step 5: Practice, Practice, and Practice! Introduce More Multiplication Tables and Multiplication Facts!
Consistent practice is the cornerstone of mastering multiplication. Once students are comfortable with the basic idea of forming and reading multiplication tables, gradually introduce more challenging tables, such as 6, 7, 8, and 9, to build their fluency. Encourage daily practice with a variety of engaging activities to reinforce multiplication facts.
Ways to Reinforce Times Tables and Multiplication Facts:
i) Sing or chant times tables using fun tunes or rhymes to make them memorable.
ii) Create a matching game where your child pairs problems (e.g., 3 × 4) with their answers.
iii) Times Tables Games: In these games, kids will master multiplication facts of 2-12 using gamified challenges, number line jumps, multiplication charts, and fill-in-the-blank challenges.
Let’s dive into multiplication facts and times tables!
Begin here
iv) Roll two dice, multiply the numbers, and say the answer aloud.
Step 6: Teach the 3 Important Properties of Multiplication: Commutative, Associative, and Distributive
Multiplication is also commutative, like addition. It means that the order of factors doesn’t change the answer.
Simply put, you can multiply two numbers in any order, and the answer will be the same. For example, the answer for 2 × 5 or 5 × 2 will be the same 10.
This property can show your students that multiplication is easier than it looks.
Ways to Reinforce Commutative, Associative, and Distributive Properties of Multiplication:
i) Commutative Property: Ask your child to create two arrays using counters or marbles: one for the fact 3 × 5 and another for 5 × 3. Count the total number of objects in each case. Also, ask them to fill in missing numbers to complete turn-around facts.
ii) Associative Property: Write equations like (3 × 2) × 4 and 3 × (2 × 4) and solve to verify they’re equal. Discuss how you can group numbers in any way and still get the same answer.
iii) Distributive Property: Discuss how we can “distribute” the multiplication sign across terms within parentheses, over addition or subtraction. e.g., Write 4 × (3 + 2) and show it’s the same as (4 × 3) + (4 × 2).
iv) Print these engaging worksheets and reinforce these three multiplication properties through bite-sized exercises:
Practice the commutative, associative, and distributive property of multiplication!
Begin here
Step 7:. Show the Relationship between Tables and Discuss Patterns
Another simple step to teaching multiplication is showing your class the relationships between tables.
When students learn tables up to 8, they already encounter multiples of 9 in other tables.
1 × 9 = 9
2 × 9 = 18
3 × 9 = 27
and so on.
This reduces the need to memorize the table of 9 separately. Help kids understand how to look for multiplication facts in tables. This small relief can help to motivate students when they struggle with multiplication.
Multiplication tables are filled with patterns that make learning easier and more fun for students:
- Table of 2: All results are even numbers.
- Table of 5: Results alternate between 0 and 5 (e.g., 5, 10, 155, 10, 155, 10, 15).
- Table of 9: The digits in each result add up to 9 (e.g., 9 × 3=27, 2 + 7=9).
- Symmetry: 3 × 4 = 12 is the same as 4 × 3 = 12.
Step 8: Break Down the Number to Simplify the Problem
If your students struggle with big number multiplication, you can show them how to break down the number.
For example, instead of multiplying 8 x 9, they can multiply as 8 x (5 + 4).
They can implement the distributive property this way,
(8 × 5) + (8 × 4) = 40 + 32 = 72.
Step 9: Tell Them the the Relationship Between Multiplication and Division
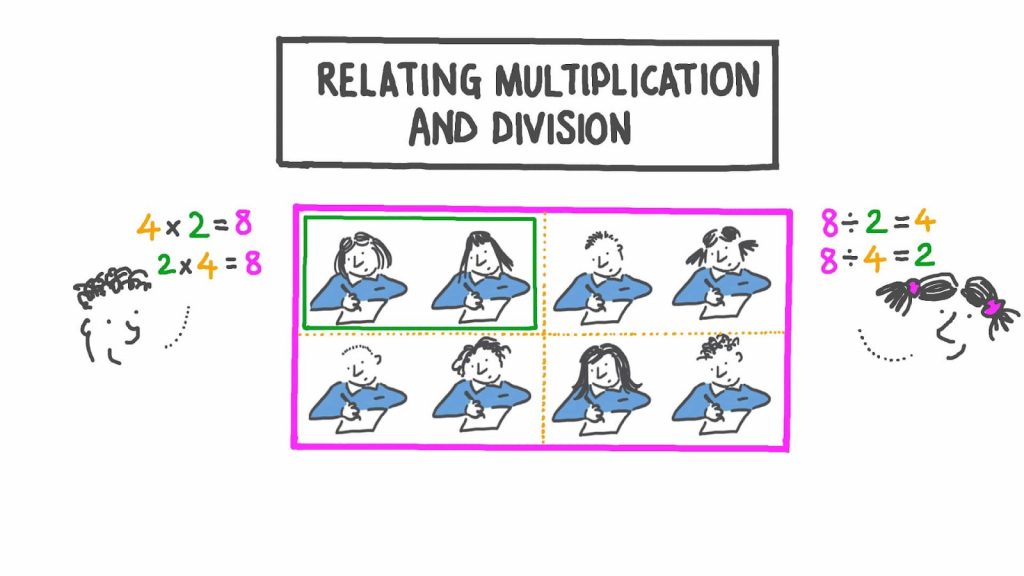
This is where you can also teach the relationship between multiplication and division. Help students understand that multiplication and division are inverse operations.
For example, if 4 × 5 = 20, then 20 ÷ 5 = 4. Pose questions such as 4 times what number is 20? Ask them to take 20 counters and place them across 4 rows. Ask: How many counters can you see in each row? It’s 5.
Step 10: Use Visuals: Introduce the Area Model Method for 2 × 2 Multiplication.
Many studies have confirmed that students learn better through visuals. So, using visual learning aids is one of the best ways to teach multiplication to struggling students.
For example, students can learn multiplication through animated games. The games let students understand the reason behind multiplication. Plus, visuals help in learning tables faster.
Area model multiplication allows students to visualize multiplication as the area of a rectangle. By dividing numbers into tens and ones, they can multiply each part and see how the products add up to the final answer.
For example, to multiply 23 × 12:
- Break the numbers into tens and ones: 23 = 20 + 3 and 12 = 10 + 2.
- Draw a rectangle divided into four sections.
- Label the sides with 20 and 3 on one side, and 10 and 2 on the other.
- Multiply each part:
- 20 × 10 =200
- 20 × 2 = 40
- 3 × 10 = 3
- 3 × 2 =6
- Add the partial products: 200 + 40 + 30 + 6 = 276
Encourage kids to draw and create their area models to represent multiplication problems. This hands-on activity helps them visualize the process and reinforces their understanding of place value and partial products. Moreover, note that this method is a bridge between conceptual models and the abstract algorithm.
Ways to Reinforce the Area Model Multiplication:
i) Draw and Divide a Rectangle: Have your child draw a rectangle, split it into sections based on place value (e.g., 23 × 14 becomes 20 + 3 and 10 + 4), and label each section with partial products.
ii) Use Graph Paper: Let your child use graph paper to create and fill in area models for problems, ensuring neat and proportional sections.
iii) Area Model Multiplication Worksheets: In these activities, kids will learn to create and shade area models, fill in the missing partial products to complete the models, and break the expressions to find the product.
Practice area model multiplication with printable worksheets!
Begin here
Step 11: Standard Algorithm for Multiplication
Introduce the standard algorithm step-by-step, emphasizing the importance of place value and regrouping. Practice with simple problems and gradually increase the difficulty to solidify understanding.
Ways to Reinforce the Standard Algorithm:
i) Lined Paper Practice: Use lined paper turned sideways to help your child align digits correctly while multiplying.
ii) Step-by-Step Charts: Create a chart breaking the algorithm into steps (e.g., multiply ones, regroup, move to tens) for guided practice.
iii) Complete the Problem: Write down a solved example with boxes to fill in missing numbers. Ask your child to figure out the missing numbers by examining the steps.
iv) Games: In these games, kids will enjoy solving multiplication problems involving up to 4-digit numbers using the standard algorithm.
Play and solve multi-digit multiplication problems!
Begin here
6 Fun Activities to Teach Multiplication to Students Who Struggle to Understand the Concept

To make multiplication easy for your students, you need to go beyond the regular teaching strategies. To make learning multiplication enjoyable and simple, here are some fun learning activities:
1. Fun Online Multiplication Games
Multiplication can feel like a challenging hurdle for many students, but turning it into a game can transform learning into an interactive experience.
Here are online multiplication games covering topics such as multiplication strategies, times tables, multiplication properties, multiplying by multiples of 10, estimating products, and more.
Begin here
- These games cater to a variety of skill levels and learning needs, ensuring all students can participate and progress.
- These games can be assigned to kids with a single click.
- They work perfectly as a warm-up activity, a centerpiece for the day’s lesson, or as part of a structured learning plan.
- You can access detailed analytics, showing where students excel and where they may need extra support. This empowers teachers to tailor their instruction to individual needs while making multiplication a fun and manageable part of math learning.
2. Multiplication on Calculator
Play a fun calculator activity to help kids find multiples of a number. For example:
- Use the calculator to find multiples of 5 (5, 10, 15, 20) and ask students to observe patterns.
- Generate multiples and have students skip count along with the calculator.
3. Multiplication Songs
Every kid loves music. And it’s so much easier to learn anything that rhymes and has beats. So, you can find some good multiplication songs and play them in your class for fun math learning. You could even encourage the students to sing along as they learn.
You can find various multiplication songs on YouTube with animated videos. Some of the best multiplication song channels and websites are:
4. Multiplication Worksheets
Practice is key to mastering multiplication, and worksheets are an excellent tool for reinforcement. They provide structured practice and help students solidify their skills at their own pace. What better way to ensure regular practice than through well-designed worksheets? They’re especially helpful for students who benefit from repetitive problem-solving and focused time to work independently. Here are some fun worksheets to assign to your class:
Begin here
5. Card Games
You can also use cards to teach multiplication to your students. Multiplication War is an old yet fun car game that can make multiplication learning fun.
Here’s how it works:
This game has two players. The cards are dealt face down in two piles by one student after they have been shuffled. Both students flip over the top card from their face-down pile after counting down (3, 2, 1, GO!).
The set is won by the first pupil, who correctly multiplies both numbers on the cards. When all of the cards have been used, the student with the most sets wins.
Be sure to assign a number to the Ace, Queen, and King if you plan to use them from the deck. For instance, the Ace might be worth zero, the Jack might be worth one, the Queen might be worth eleven, and the King might be worth twelve. Don’t forget to take out the jokers!
6. Multiplication Bingo
A fun twist on the classic bingo game, designed to practice multiplication. It helps kids match problems with their answers while having fun.
Here is how it works:
Create bingo cards filled with random multiplication answers like 12, 24, or 36. The teacher or facilitator calls out multiplication problems, such as “6 x 6,” and players search for the correct answer on their bingo cards. If they have the answer, they mark it. The first player to complete a row, column, or diagonal shouts “Bingo!” and wins the game.
7. A Friendly Math Competition
Competition is the best way to motivate students. You can host a multiplication fact competition in your class and offer a fun reward to encourage students to learn multiplication.
Here’s how it works:
- Split your class into two teams.
- Make two lines of students, with one line representing each team, and have them face one another.
- The instructor may hold up an equation or call out a multiplication fact.
- A student in the first pair (the kids facing each other) shouts out the solution.
- A point is awarded to the student who responds correctly in the first place.
- The instructor moves on to the following pairing as the students both sit.
- The instructor continues this until every student in the line has been addressed.
- The row that scores the most wins.
You can give the role of scorekeeper to a student if you have an odd number of students in your class. Pairing students at the same academic level to compete against one another can benefit them, too.
Related Reading: Easy Ways to Make Math Fun for Kids
Conclusion
As you can see, using a creative approach to teaching multiplication to your students will help them learn and retain the concepts.
Innovative methods can make math simple and interesting for your students. So, use visuals, games, activities, and different strategies to make multiplication fun.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can I teach multiplication to students who have math anxiety?
Here’s how to teach multiplication to students who seem overwhelmed with the topic in 4 easy steps:
- Step 4: Work on mastering each table separately.
- Step 1: Divide the information into manageable portions.
- Step 2: Use a straightforward visual to provide context to the fact.
- Step 3: Show the student how to use the simpler facts as a springboard for the more difficult ones.
How can I teach my ADD/ADHD students how to multiply?
Lay out the cards one at a time for your students to multiply after explaining what you want them to practice (such as 9 x tables) and setting a timer for one minute. Give them the answers to any questions they get wrong so they will have a better chance of answering correctly the next time the number is called. Target 20–30 facts per minute.
How do you teach multiplication to a third grader?
Students can express multiplication issues using arrays. They can use beads, blocks, bottle caps, paper clips, or other objects to complete them on a grid or just on their desks.
When should a child start learning multiplication facts?
Most experts concur that children start learning their tables between the ages of five and eight. They can begin to comprehend how their numbers interact with one another as they start to become more conscious of their numbers.










































































