What Are Plane Shapes?
In geometry, plane figures or plane shapes, also known as two-dimensional shapes, are fundamental geometric figures that exist in a flat, two-dimensional plane.
Plane shapes do not have thickness or depth unlike three-dimensional shapes, making them ideal for representation on a flat surface, such as a piece of paper. These shapes are the building blocks of geometry and are extensively studied in mathematics.
Recommended Games
Definition of Plane Shape
Plane shapes can be defined as two-dimensional geometric figures that exist on a flat surface, known as a plane.
These shapes have only length and width, with no depth or thickness. They are characterized by their boundaries, which can be made up of straight sides or curved lines. Plane shapes examples include polygons (triangles, quadrilaterals), circles, and other curvilinear figures.
Recommended Worksheets
Different Plane Shapes in Geometry
In geometry, there are several different types of plane shapes. Here are some of the most commonly discussed ones:
| Triangles | Triangles are closed plane shapes with three sides and three angles. |  |
| Quadrilaterals | Quadrilaterals are closed plane shapes with four sides and four angles. Common examples are squares, rectangles, and parallelograms. |  |
| Circles | Circles are plane shapes with a curved boundary consisting of all points equidistant from a fixed point called the center. |  |
| Ovals | Oval shape is a plane shape that resembles the shape of an egg or a squashed circle. |  |
| Different Polygons | Polygons are closed plane shapes with at least three sides. Polygons with three sides: TrianglesPolygons with four sides: QuadrilateralsPolygons with five sides: PentagonsPolygons with six sides: Hexagonsetc. | 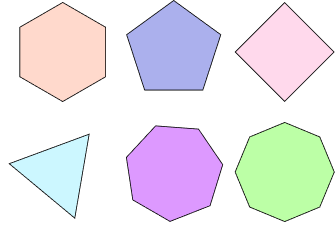 |
What Are Open and Closed Shapes?
In geometry, plane shapes can be categorized as open or closed based on their boundaries.
- Closed Plane Shapes: Closed shapes are plane figures that have a complete and continuous boundary that forms a closed loop. This means that the shape does not have any openings (holes) or breaks in its boundary.
Examples of closed plane shapes include polygons (such as triangles, squares, pentagons), circles, ellipses, etc. These shapes enclose a finite area within their boundaries.
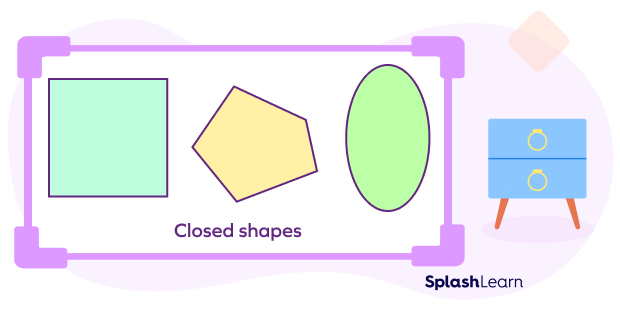
- Open Plane Shapes: Open shapes are figures that do not have a complete and continuous boundary. They have one or more openings or breaks in their boundary, which means they do not form a closed loop.
Examples of open plane shapes include lines, line segments, rays, and curves that do not form closed loops (like a curve with endpoints that do not meet). Open plane shapes do not enclose any area since they lack a complete boundary.
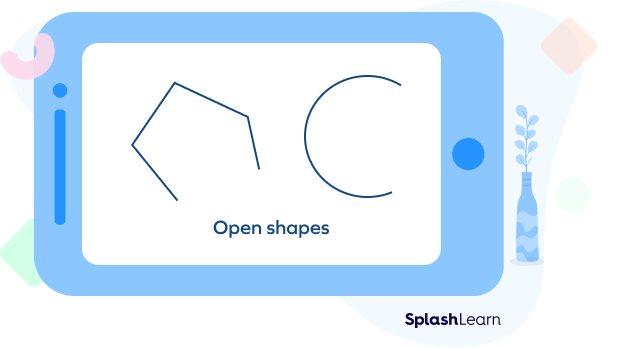
Polygons
Polygons are most commonly discussed plane shapes apart from circles.
In geometry, a polygon can be defined as a flat or plane, two-dimensional closed shape bounded with at least three sides.
It does not have curved sides. The sides of a polygon are also called its edges. The points where two sides meet are the vertices (or corners) of a polygon.
The types of polygons can be categorized into three major forms: regular or irregular, concave or convex, and simple or complex.
Regular Polygons and Irregular Polygons:
| Regular Polygons | Irregular Polygons |
|---|---|
| A regular polygon has all sides of equal length and all interior angles of equal measure. Examples include equilateral triangles, squares, and regular pentagons. | An irregular polygon has sides of different lengths and/or interior angles of different measures. Examples include scalene triangles, rectangles, and irregular hexagons. |
 | 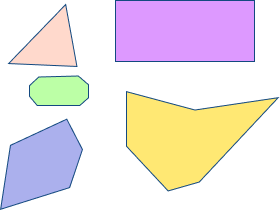 |
Convex Polygons and Concave Polygons:
| Convex Polygons | Concave Polygons |
|---|---|
| A convex polygon has all its interior angles less than 180 degrees. All sides of a convex polygon lie on the same side when any two points inside the polygon are connected. Examples include equilateral triangles, squares, and regular hexagons. | A concave polygon has at least one interior angle greater than 180 degrees. It has at least one “caved-in” or “dented” portion. Examples include a star shape or a crescent shape. |
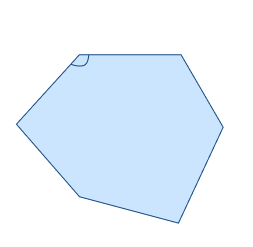 | 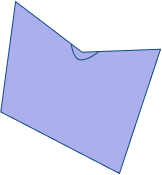 |
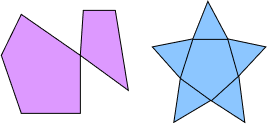
Simple Polygons and Complex Polygons
| Simple Polygons | Complex Polygons |
|---|---|
| A simple polygon is non-self-intersecting, meaning that its sides do not cross over each other. It forms a single continuous shape. Examples include triangles, rectangles, and regular polygons. | A complex polygon is self-intersecting, meaning that it has sides that cross over each other, creating additional interior regions within the polygon. Examples include shapes with holes or overlapping sides. |
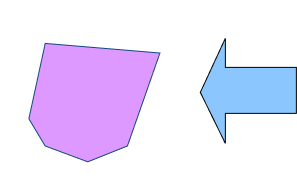 |  |
Sides and Vertices of Plane Shapes
Sides: In plane shapes, the sides refer to the straight line segments that form the boundary of the shape.
Vertices: The corners or the points where the sides meet are called the vertices.
It’s important to note that some plane shapes, such as circles, do not have straight sides or corners/vertices. Instead, they have a continuous curved boundary. However, polygons are the plane shapes that have distinct sides and corners/vertices that define their structure.
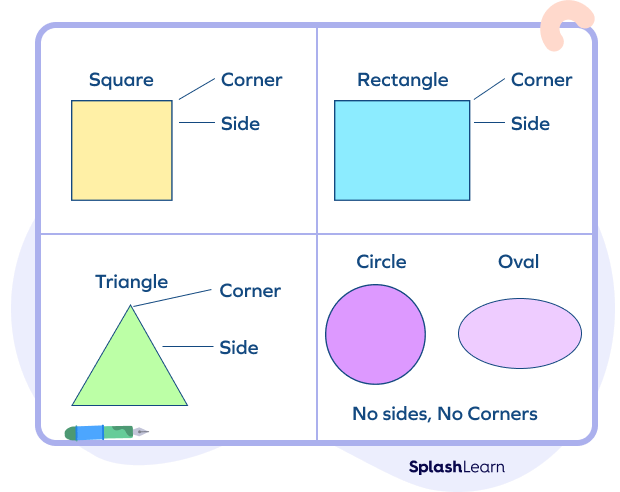
No sides, No Corners
Plane Shapes vs. 3D Shapes
| Aspect | Plane Shapes | 3D Shapes |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | Two-dimensional | Three-dimensional |
| Flat or Solid | Flat, occupy a single plane | Solid, occupy space |
| Depth | No depth or thickness | Have depth and thickness |
| Examples | Triangles, rectangles, circles | Cubes, spheres, cylinders |
| Volume | No volume, as they are flat | Have volume, representing the amount of space they occupy |
| Projection | Represented on a flat surface | May have different views from different angles |
Facts about Plane Shapes
- Plane shapes, also known as 2D shapes, are flat figures that exist in a two-dimensional space, with length and width but no depth.
- A polygon is a closed plane figure with straight sides. Examples of polygons include triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, and so on.
- Circles are another type of plane shape. They are perfectly round and have no straight sides or angles. Circles are not polygons.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about plane shapes. Learning about plane shapes provides a solid foundation for geometry, enhances problem-solving skills, and has practical applications in numerous fields. It promotes critical thinking, spatial reasoning, and effective communication, making it both useful and necessary in education and beyond. Now let’s solve some examples and practice problems for better understanding.
Solved Examples on Plane Shapes
Example 1: Classify the following plane shape as open, closed, simple, or complex.

Solution:
The shape crosses itself.
So, it is not simple. It is a complex shape.
It forms a closed loop.
So, it is a closed shape. It is not an open shape.
Example 2: Which of the following are not plane shapes?
Circle, Sphere, Cube, Square, Cuboid, Triangle
Solution:
Sphere, cube, cuboid are 3D shapes or geometric solids.
So, they are not plane shapes.
Circle, square, triangle are plane shapes.
Example 3: Which of the following is not an open shape?
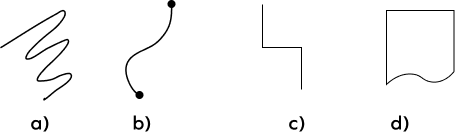
Solution:
Shapes a, b, and c have different starting and end points. They do not have any interior.
The shape d does not have any open ends, so it is a closed shape. It forms a closed loop and has an interior.
Example 4: How many sides, vertices does this shape have? Is the shape closed or open?
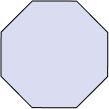
Solution:
First, we count the number of straight line segments in the shape.
There are eight straight lines connected to each other, making an octagon.
As this octagon’s outline may be traced without any gaps, it is a closed shape.
Practice Problems on Plane Shapes
Plane Shapes - Definition, Types, Solved Examples, Facts, FAQs
What are plane shapes in mathematics?
Plane shapes, also known as two-dimensional shapes, are fundamental geometric figures that exist in a flat, two-dimensional plane.
Which plane shape has no sides?
A circle is a plane shape with a curved boundary and no sides. It consists of all points equidistant from a center point.
Which shape has three sides and three angles that add up to 180 degrees?
A triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles. The sum of the interior angles of any triangle always adds up to 180 degrees.
What do we call plane shapes with four sides?
A pentagon has 5 sides, a hexagon has 6 sides, while a circle is a curved figure with no straight sides. Therefore, the term used to describe plane shapes with four sides specifically is a quadrilateral.
Which of the following is an open shape?

Figure b has different starting and ending points. Therefore, it is an open shape.
Frequently Asked Questions about Plane Shapes
How do symmetry and rotational symmetry apply to plane shapes?
Symmetry refers to the balanced arrangement of elements. Plane shapes can exhibit symmetry, such as line symmetry (mirror image) or rotational symmetry (ability to rotate around a central point and maintain the same appearance).
What are some real-world applications of plane shapes?
Plane shapes have various applications in real life, including architecture and design (floor plans, blueprints), art (paintings, sculptures, tessellations), map projections, and more.
How do congruent and similar plane shapes differ?
Congruent shapes are identical in shape and size, while similar shapes have the same shape but can differ in size.
How do plane shapes relate to three-dimensional shapes?
Plane shapes are two-dimensional and can be considered as the faces of three-dimensional shapes. Three-dimensional shapes are composed of plane shapes interconnected in a three-dimensional space.
What is the difference between a polygon and a polyhedron?
A polygon is a two-dimensional plane shape with straight sides, while a polyhedron is a three-dimensional solid shape with flat polygonal faces, edges, and vertices.
What is the relationship between the area and perimeter of a plane shape?
The area of a plane shape refers to the measure of the space enclosed within its boundaries, while the perimeter is the total length of its boundary. There is no direct relationship between the area and perimeter of a shape; they are separate measurements used to describe different aspects of the shape.
How can I determine if two plane shapes are similar?
Two plane shapes are similar if their corresponding angles are equal, and the ratios of their corresponding side lengths are proportional.
What are flat shapes?
Flat shapes and plane shapes refer to the same concept.Both terms are used interchangeably to describe two-dimensional figures that exist on a flat surface or plane. These shapes have length and width but no depth.




































