What Is the Additive Inverse of a Number?
Additive inverse of a number is a number that, when added to the original number, gives the sum of 0. In simple words, the sum of a number and its additive inverse is always 0.
Mathematically, the additive inverse of a real number n is denoted as – n.
Similarly, the additive inverse of – n is n.
n + ( – n) = 0 for every real number n.
In simple words, the additive inverse of a number is the opposite or negative of that number. In general, we can study the concept of additive inverse for integers, rational numbers, real numbers, etc. Note that the number 0 is known as the additive identity.
Additive inverse examples:
- The additive inverse of 7 is – 7, since 7 + (– 7) = 0.
- The additive inverse of –10 is 10.
- The additive inverse of – 99 is 99, since (– 99) +99 = 0.
- The additive inverse of 0 is 0 itself, because 0 + 0 = 0.
Recommended Games
Additive Inverse Definition
The additive inverse of a number is the number that, when added to the given number, results in the sum of 0.
The additive inverse of a number is also called the opposite or the negation (or negative) of that number.
Additive Inverse Property
If the sum of two real numbers is zero, then each real number is said to be the additive inverse of the other.
In simple words, if a + b = 0, where a and b are real numbers, then we can say that
- a is the additive inverse of b, and
- b is the additive inverse of a.
Additive Inverse on a Number Line
On a number line, we can easily find the additive inverse of a number. Note down the distance of the given number from the origin. Now, mark the point to the opposite direction of 0, which lies at the same distance.
In other words, 0 is the midpoint of the line segment joining the given number and its additive inverse on a number line.
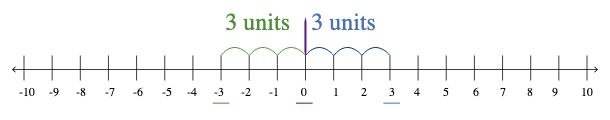
Additive Inverse Formula
Additive inverse of x = 0 – x
Additive inverse of x = ( – 1) $×$ x
How to Find the Additive Inverse of a Number
We can find the additive inverse of a number using different methods.
Formula 1: Subtraction method
Let x be any real number. To find the additive inverse of x, simply subtract x from 0.
Additive inverse of x = 0 – x
Examples:
Additive inverse of 6 = 0 – 6 = – 6
Additive inverse of – 9 = 0 – ( – 9) = 9
Formula 2: Multiplication method
Let x be any real number. To find the additive inverse of x, simply multiply x with –1.
Additive inverse of x = (– 1) $×$ x
Examples:
Additive inverse of 1 = ( –1 ) $×$ 1 = – 1
Additive inverse of – 78 = (– 1) × (– 78) = 78
Additive Inverse: Properties
- – ( – x) = x
- – (x + y) = – x – y
- –(x – y) = y – x
- – ($\frac{x}{y}$)= $\frac{x}{– y}$
- $– (\frac{– x}{y})= \frac{x}{y}$
- – (x + y)] = (– x) + (– y)
- – (x – y) = ( – x) + y
- (– x) $\times$(– y)= x y
- x $\times$ (– y) = (– x) y =– (x $\times$ y)
Additive Inverse of Different Numbers
Additive inverse of natural numbers and whole numbers
Natural numbers are counting numbers, defined by the set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, … }.
Whole numbers are the set of natural numbers with 0 or {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …).
Natural numbers are positive. Whole numbers (except 0) are also positive. Thus, the additive inverse of any natural numbers or a whole number (except 0) is always negative.
Examples:
- Additive inverse of 0 is 0.
- Additive inverse of 1 is -1.
- Additive inverse of 5783 is -5783.
- Additive inverse of 49 is -49.
Additive inverse of integers
The set of integers consists of positive integers, negative integers, and 0.
Integers = {…,-3,-2,-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …}
The additive inverse of negative integers is always positive.
The additive inverse of positive integers is always negative.
Additive inverse of 0 is 0.
Examples:
- The additive inverse of -10 is -(-10) = 10.
- The additive inverse of 42 is -(42) = -42.
- The additive inverse of -42 is 42.
Additive Inverse of Fractions
A fraction is a number represented as $\frac{x}{y}$, where x and y are whole numbers, and y is not equal to 0.
The additive inverse of a fraction $\frac{x}{y}$ is $\frac{-x}{y}$.
Examples:
- Additive inverse of $\frac{7}{8}$ is $\frac{-7}{8}$.
- Additive inverse of $\frac{6}{7}$ is $\frac{-6}{7}$.
Additive Inverse of Rational Numbers
Rational numbers are of the form $\frac{p}{q}$, where p and q are integers, and q is not equal to 0.
The additive inverse of a rational number $\frac{p}{q}$ is $\frac{-p}{q}$.
Examples:
- Additive inverse of $\frac{5}{9}$ is $\frac{-5}{9}$.
- Additive inverse of $\frac{-1}{7}$ is $\frac{1}{7}$.
Additive inverse of Decimals
For any decimal x, its additive inverse is -x.
For instance, the additive inverse of 0.25 is -0.25, as 0.25 + (- 0.25) = 0.
Additive Inverse and Multiplicative Inverse
| Additive Inverse | Multiplicative Inverse |
|---|---|
| Additive inverse is a number that, when added to the original number, the sum is 0. | Multiplicative inverse is a number that, when multiplied with the original number, the product is 1. |
| The additive inverse of a number is the negative or opposite of that number. | The multiplicative inverse of a number is the reciprocal of that number. |
| The sum of a number and its additive inverse is always 0. | The product of a number and its multiplicative inverse is always 1. |
| Additive inverse of 0 is 0. | 0 does not have a multiplicative inverse. |
| For any real number n, its additive inverse is -n. | For any non-zero real number n, its additive multiplicative inverse is $\frac{1}{n}$. |
Facts about Additive Inverse
- The additive inverse of the additive inverse is the original number.
- The additive inverse of 0 is 0 itself.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about the concept of additive inverses and how they play a crucial role in mathematics. Understanding the additive inverse allows us to work with negative numbers more effectively and solve a variety of mathematical problems. Let’s solidify our understanding by practicing a few examples and attempting MCQs for better comprehension.
Solved Examples on Additive Inverse
1. What is the additive inverse of 12345?
Solution:
Given number = 12345
Additive inverse of 12345 = 0 – 12345 = -12345
2. What is the additive inverse of $\frac{-10}{13}$?
Solution:
The additive inverse of $\frac{x}{y}$ is $\frac{-x}{y}$.
Additive inverse of $\frac{-10}{13} = \;-\; (\frac{-10}{13}) = \frac{10}{13}$
Thus, the additive inverse of $\frac{-10}{13}$ is $\frac{10}{13}$.
3. The additive inverse of a number is -6. Find the number.
Solution:
Let x be the number.
Additive inverse of x = -x
It is given that the additive inverse is -6.
Thus, – x = -6
x = 6
The required number is 6.
4. Is 3x + 5 additive inverse of – 3x – 5?
Solution:
The sum of a number and its additive inverse is 0.
Let’s find the sum of 3x + 5 and – 3x – 5.
(3x + 5) + (- 3x – 5)= 3x + 5 – 3x – 5 = 0
So, 3x + 5 is the additive inverse of -3x – 5.
Practice Problems on Additive Inverse
Additive Inverse: Definition, Formula, Properties, Facts, Examples
What is the additive inverse of the additive inverse of 3?
Additive inverse of $3 = \;-\;3$
Additive inverse of $\;-\;3 = 3$
Thus, the additive inverse of the additive inverse of 3 is 3.
What is the additive inverse of 0?
Additive inverse of 0 is 0.
To find the additive inverse of a non-zero real number,
All options are different ways to find the additive inverse of a number.
The sum of a number and its additive inverse is _______.
The sum of a number and its additive inverse is 0.
What is the multiplicative inverse of a number whose additive inverse -0.6?
Additive inverse of a number $= \;-\;0.6$
Thus, the number $= 0.6$
Multiplicative inverse of $0.6 = \frac{1}{0.6} = \frac{10}{6} = \frac{5}{3}$
Frequently Asked Questions on Additive Identity
What is the additive inverse of 0?
The additive inverse of 0 is 0 itself.
Is the additive inverse all whole numbers negative?
Except for 0, the additive inverse of all other whole numbers (natural numbers) is always negative, since all the natural numbers are positive.
Is additive inverse the same as additive identity?
The sum of a number and its additive identity is the number itself, whereas the sum of a number and its additive inverse is 0.


















