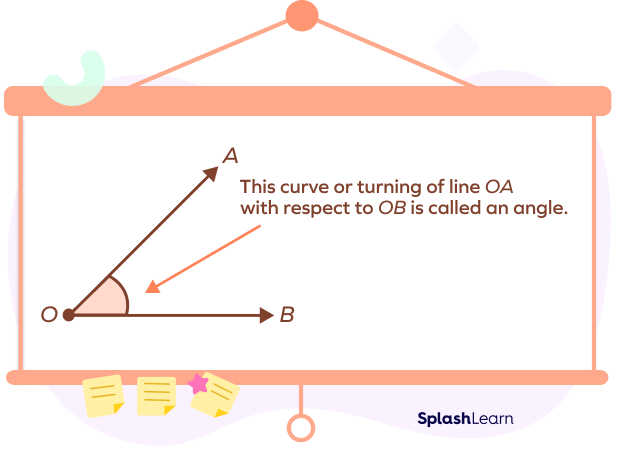
What Is an Angle?
When two straight lines or rays meet at a common endpoint, an angle is formed. The common point of contact of the two rays is called the vertex of an angle. We use the symbol ∠ to represent an angle. We use degrees (°) to measure an angle using a protractor. For example, 45 degrees is represented as 45°.
There are different types of angles:
- Acute angle
- Obtuse angle
- Right angle
- Straight angle
- Reflex angle
Recommended Games
What Is a Straight Angle?
In geometry, a straight angle is defined as an angle that is equal to 180 degrees. The reason it is called a straight angle is because it appears as a straight line. In other words, it is an angle whose sides lie in opposite directions from the vertex in the same straight line.

Recommended Worksheets
Straight Angle Examples
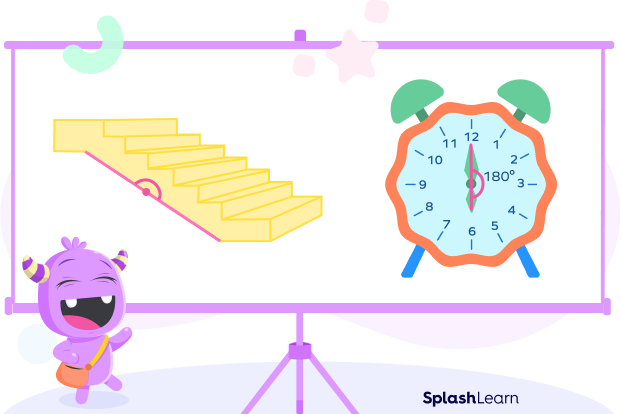
Some of its examples in our day-to-day life are:
- A flat surface has an angle of 180 degrees.
- A plane inclined staircase.
- The angle between the minute hand and hour hand at 6:00.
- The ruler we use.
Properties of a Straight Angle
Its properties are as follows:
- It is formed by rotating one ray by 180° with respect to another ray.
- It reverses the direction of a point.
- It is exactly half of a revolution, i.e., it is half of a complete angle.
- It can also be formed by joining two right angles, i.e., 90° + 90° = 180°.
- We denoted the straight angle as π.
- It is also known as flat angle.
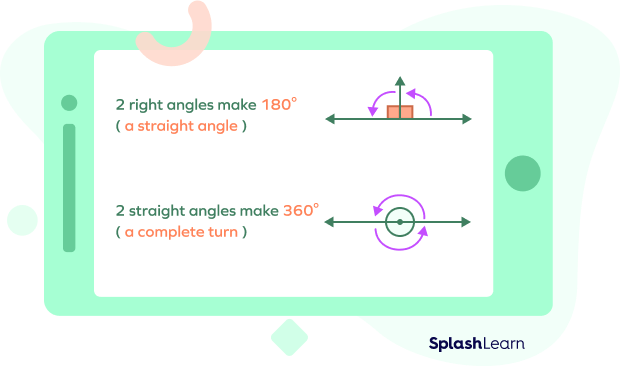
Straight Angle Pair
A straight angle pair is a pair of angles that form a straight line. The sum of two or more angles that are in this pair is always equal to 180°. We also call them linear pairs of angles.
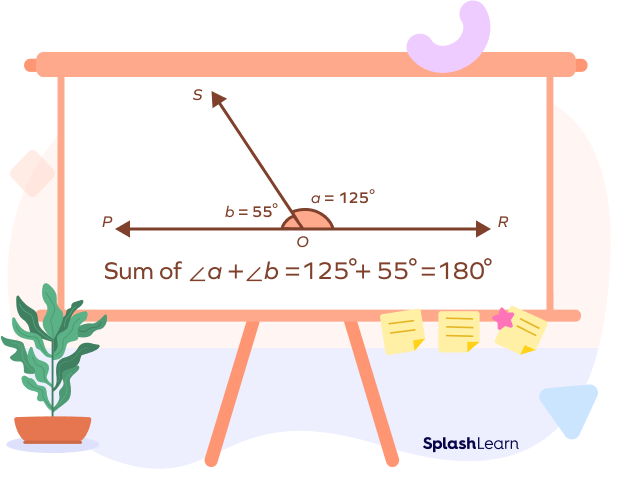
The image given above shows two angles ∠a = 125° and ∠b = 55°, which together form 180°. The straight angle has a common arm and a common vertex. In the above figure, OS is the common arm and O is the common vertex.
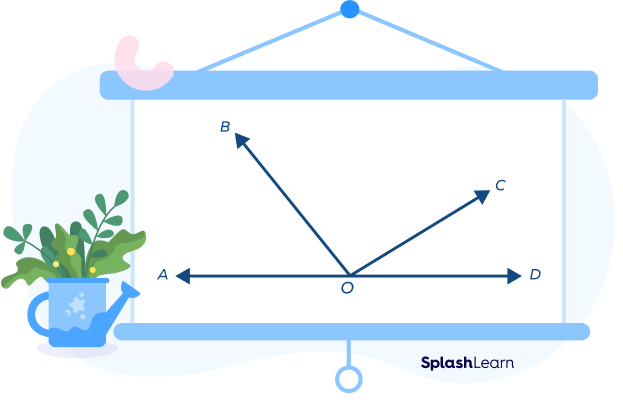
Sometimes there are 3 angles on the straight line. For example, in the figure given below, ∠AOB + ∠BOC + ∠COD = 180°
Solved Examples
Example 1: Find the value of ∠COD in the following diagram.
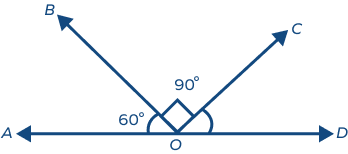
Solution: ∠AOD is a straight angle.
∠AOB + ∠BOC + ∠COD = 180°
60° + 90° + ∠COD = 180°
∠COD = 30°
Example 2: There are _____ 30° in a straight angle.
Solution: A straight angle = 180°
180°30°=6.
Example 3: Find all the combinations forming straight angles in the following figure.
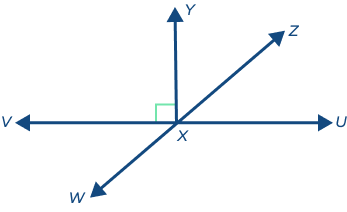
Solution: Straight angles are:
∠VXY, ∠YXZ and ∠ZXU
∠VXY, and ∠YXU
∠VXZ, and ∠ZXU
∠VXW and ∠WXU
∠WXV, ∠VXY and ∠YXZ
∠WXV, and ∠VXZ
∠WXY, and ∠YXZ∠WXU and ∠UXZ
Practice Problems
Straight Angle - Definition With Examples
Which of the following is the measure of 2 right angles?
Two right angles = 2 ✕ 90° = 180°
Find the value of x if x + 2, x and x + 10 forms a linear pair.
$x + 2 + x + x + 10 = 180°$
$3x + 12 = 180°$
$3x = 168°$
$x = 56°$
What is not true about the straight angle?
Reflex angle is an angle lying between a straight angle and a complete angle.
What fraction of the complete angle is a straight angle?
Straight angle = 180°
Complete angle = 360°
Fraction = $\frac{180°}{360°}$=$\frac{1}{2}$
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a straight angle and a straight line?
A straight angle measures 180 degrees and a straight line is a connector of two points.
What is the difference between a pair of supplementary angles and straight angle pairs?
A pair of supplementary angles is the pair of angles whose sum is 180° but the angles may or may not be adjacent. On the other hand, a straight angle pair is the pair of angles that are always adjacent to each other and have the sum 180°.
What is the sum of the interior angle and exterior angle?
The sum of the interior angle and exterior angle is 180° as they lie on the same line.