What Is an Area Model?
An area model is a visual representation used in mathematics to illustrate multiplication and factorization concepts. It involves breaking down shapes into smaller units to better understand the relationship between numbers and their products.
The area model is a visual strategy for both multiplication and division. In multiplication, it involves representing the two factors as the dimensions of a rectangle, and the product is the area of that rectangle. For division, the area model helps visualize how a quantity is distributed into equal parts, with the quotient being the size of each part. This approach enhances understanding by connecting arithmetic operations to geometric concepts.
To understand the area model in math, we must understand the meaning of area first. The space occupied by a flat shape or surface of an object is known as area. The area of the rectangle given below is the shaded part. Area of a rectangle is the base of the area model of solving multiplication and division problems.
Area of a rectangle = Length × Width
If the rectangle has a length equal to 25 units and width 18 units, then this area can be calculated by finding the product 25 × 18. In other words, when you consider the product 25 × 18, geometrically, we can interpret it as the area of a rectangle of length 25 units and width 18 units.
Recommended Games
Area Model of Fractions
A fraction area model represents a whole shape that is split into equal parts.
Suppose we are given a model representation of a fraction. To identify the fraction, we use the following steps:
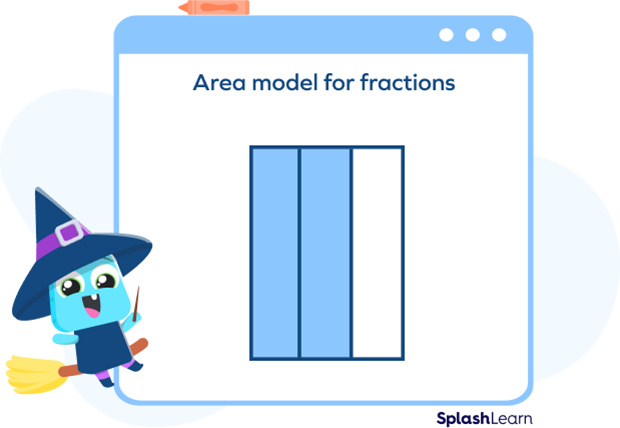
- Step 1: The whole shape is divided into equal parts. We count these numbers. We write this number as the denominator. In this example, there are 3 equal parts, so the denominator is 3.
- Step 2: Count the number of shaded shapes given in the figure. We write this number as your numerator. There are 2 shaded parts. So, the numerator is 2.
- Step 3: We write it in the form of $\frac{Numerator}{Denominator}$. In this example, we get $\frac{2}{3}$.
Recommended Worksheets
What Is an Area Model of Multiplication and Division?
In mathematics, an area model is a rectangular diagram that is used to multiply and divide two numbers or expressions, in which the factors or the quotient and divisor define the length and width of the rectangle. We can break down one large area of the rectangle into several smaller boxes, using number bonds, to make the calculation easier. Then we add to get the area of the whole, which is the product or quotient.
Area Model of Multiplication of Whole Numbers
Multiplication of 2-digit Number by 1-digit Number
Example: 65 × 7
- Step 1: Write the multiplicands in expanded form.
In this example, 65 = 60 + 5
- Step 2: Draw a 2 × 1 grid or 1 row and 2 column box.
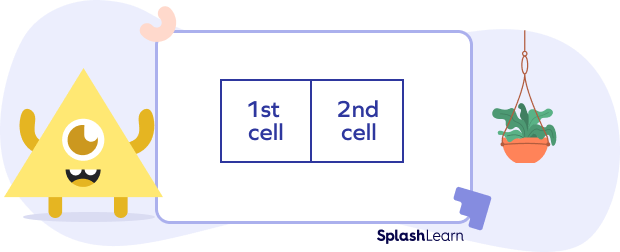
- Step 3: On the top of the grid, write “the tens and ones part of the multiplicand we expanded earlier. On the left side we write the other expanded multiplicand. In this example:
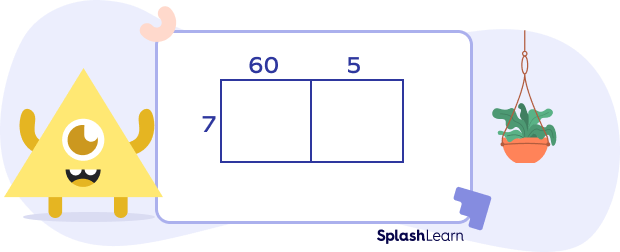
- Step 4: In the first cell, write the product of the number 7 and the tens part of the number 65. In the second cell, write the product of the number 7 and ones part of 65. In this example:
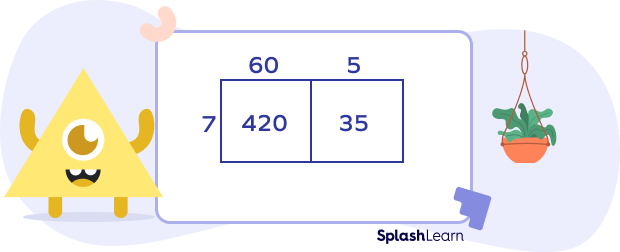
- Step 5: Add the partial products i.e. numbers in each of the cells. In this example:
420 + 35 = 455
So, we can say that 65 × 7 = 455
Multiplication of 2-Digit Number by 2-Digit Number
Example: 52 × 79
- Step 1: Write the multiplicand and multiplier, i.e., 52 and 79 in expanded form.
In this example, 52 = 50 + 2 and 79 = 70 + 9
- Step 2: Draw a grid of size 2 by 2.
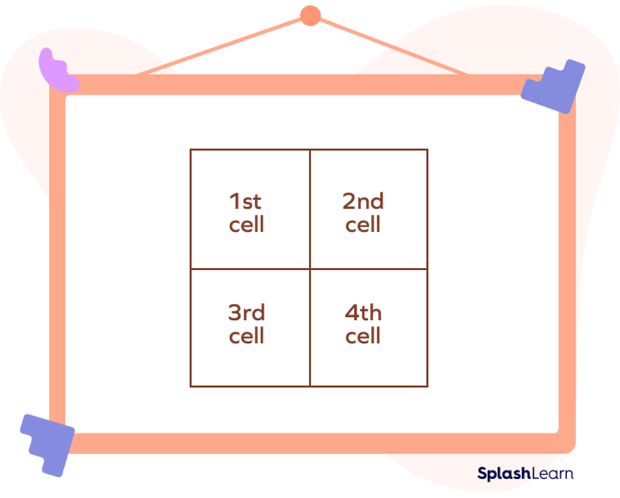
- Step 3: On the top of the grid, write the terms for one of the multiplicands. Mention the other multiplicand on the left side. In this example, we get:
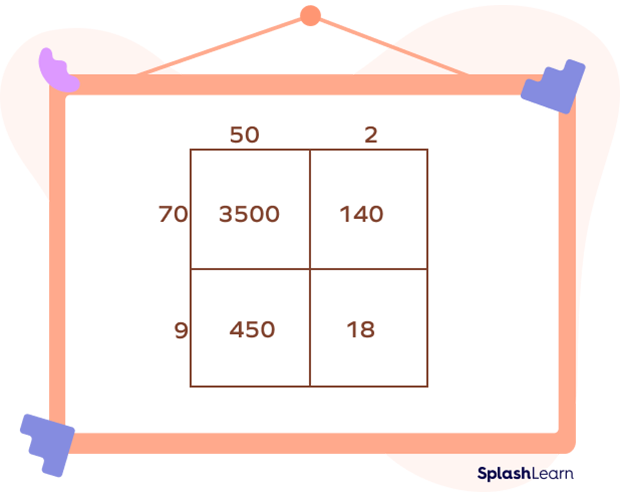
- Step 4: In the first cell, put down the product of the tens of both the numbers. In the second and third cells, put the product of the tens and ones of the numbers accordingly. In the fourth cell, put the product of the ones of both the numbers.
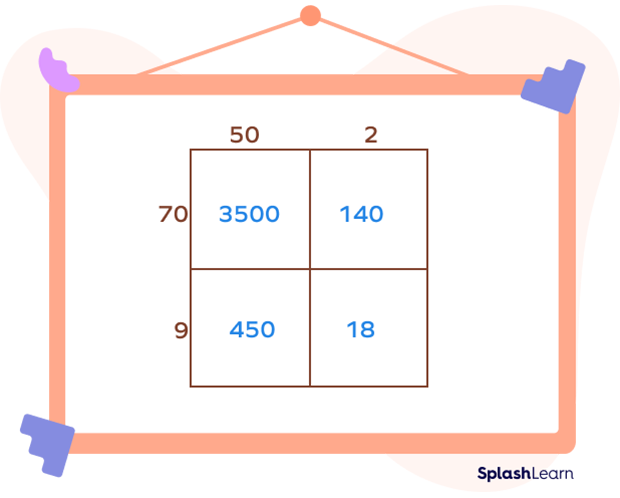
- Step 5: Add the partial products. In this example:
3500 + 140 + 450 + 18 = 4108
So, we can say that 52 × 79 = 4108
Multiplication of 3-Digit Number by 2-Digit Number
In the multiplication of a 3-digit number by a 2-digit number, we make a grid of 2 × 3.
For example: Multiply 248 × 81
248 = 200 + 40 + 8 and 81 = 80 + 1
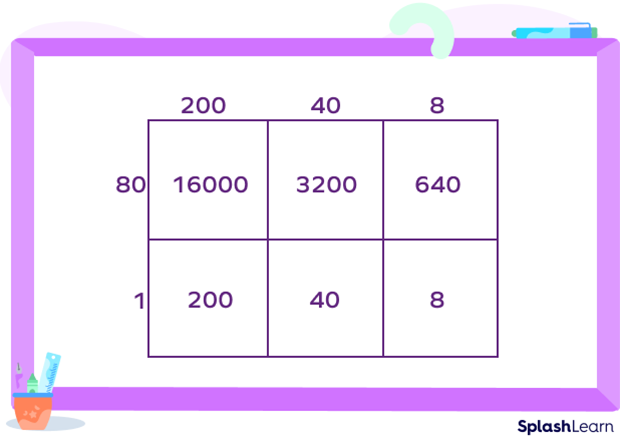
Adding the partial products, we get 16000 + 3200 + 640 + 200 + 40 + 8 = 20088
So, the product 248 × 81 = 20088
Area Model of Multiplying the Fractions
Proper Fractions
We can also multiply two proper fractions using an area model. Suppose we have to multiply $\frac{3}{4}$ and $\frac{1}{2}$, we will follow the steps given below:
Step 1: Draw a rectangle and mark length on one side and breadth on the other side. In this case, mark $\frac{3}{4}$ as length and $\frac{1}{2}$ as breadth as $\frac{3}{4} \gt \frac{1}{2}$.
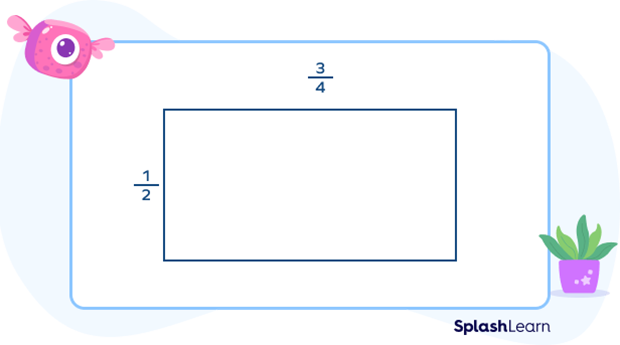
Step 2: Look at the length. Divide the length into the parts as much as the denominator and shade the parts same as the numerator. In this case, divide the length into 4 equal parts and shade 3 out of them.
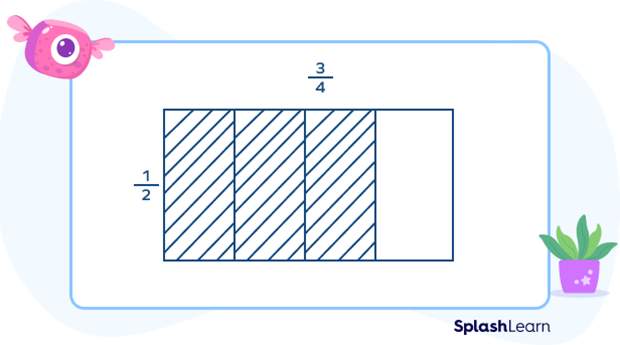
Step 3: Look at the breadth. Divide the breadth into the parts as much as the denominator and shade the parts the same as the numerator. In this case, divide the breadth into 2 equal parts and shade 1 out of them.
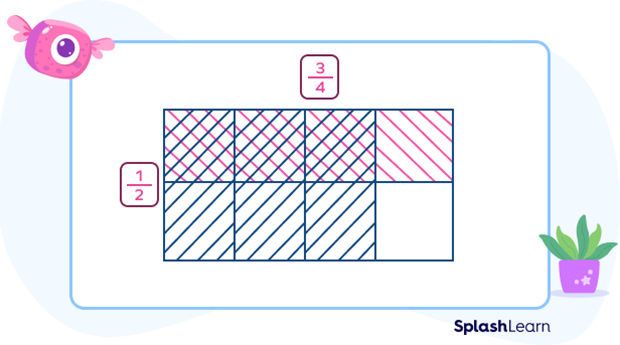
Step 4: See the common shaded parts. In this case, there are three shaded parts, so the numerator of the product is 3.
Step 5: See the total number of equal parts. In this case, the total number of equal parts are 8. So, the denominator of the product is 8.
Step 6: Write the product fraction as $\frac{Numerator}{Denominator}$. In this case, the product $= \frac{3}{8}$.
Area Model for Multiplying the Decimals
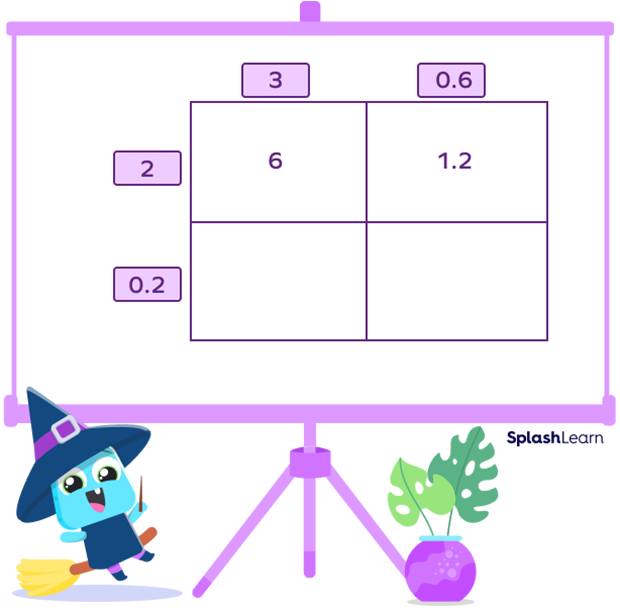
Suppose we have to multiply 3.6 and 2.2.
Step 1: Break the decimal into a whole number and decimal portion.
Here, 3.6 = 3 + 0.6 and 2.2 = 2 = 0.2
Step 2: Make a 2 × 2 grid
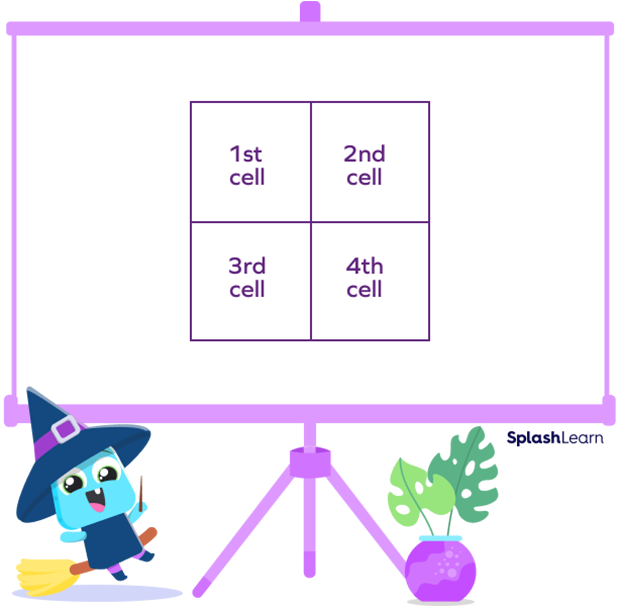
Step 3: On the top of the grid, write one of the multiplicands, and on the left side of the grid, write the other one, as mentioned in the image.
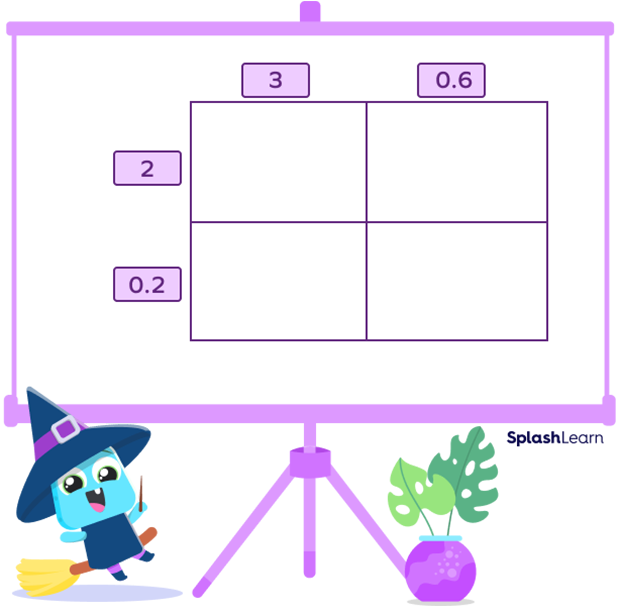
Step 4: Multiply the whole part of one multiplicand with both the parts of the second multiplicand and fill the first row. Here, we are first multiplying 2 and 3 and then, 2 and 0.6.
Step 5: Multiply the decimal part of the same multiplicand with both the parts of the second multiplicand and fill the second row. Here, we are multiplying 0.2 and 3 and then, 0.2 and 0.6.
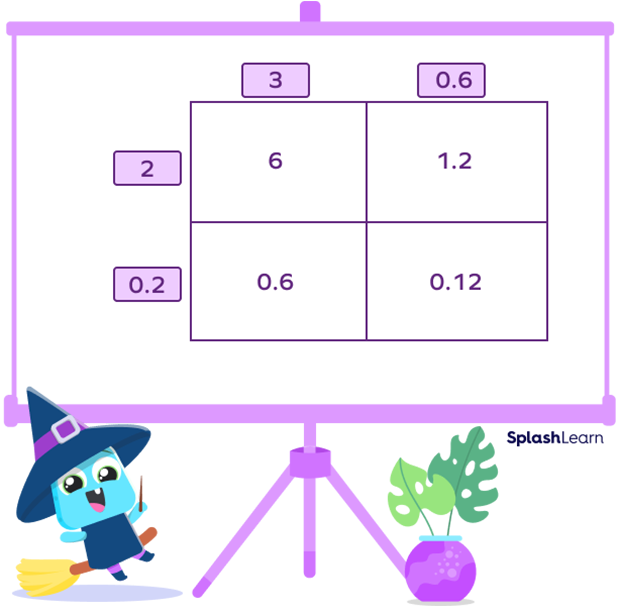
Step 6: Add the numbers in all 4 cells to find the answer.
So, 3.6 × 2.2 = 6 + 1.2 + 0.6 + 0.12 = 7.92
Area Model of Division of Whole Numbers
Area of a rectangle with the length of 48 units and a width of 21 units can be measured by multiplying 48 by 21. Similarly, a division problem like 352 ÷ 22 can be represented geometrically as the missing dimension of a rectangle with an area of 352 square units and a side of 22 units. The division is considered to be complete when the difference we get at the end is less than the divisor. The difference we are left with at the end is known as the remainder.
Division without Remainder
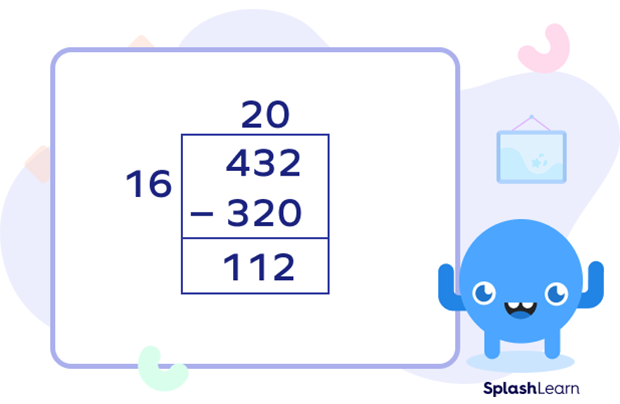
Suppose we have to divide 432 by 16.
- Step 1: Write the dividend inside the box and the divisor outside the box.
In this example:

- Step 2: We will find a number divisible by 16 and less than or equal to 43. We get 32. We will add 0 after it. After eliminating 320 from 432, we get 112. And we will write quotient on the top, i.e., 20.
- Step 3: We move to the next box. Now we find a number divisible by 16 and less than equal to 112. We get 16 × 7 = 112.
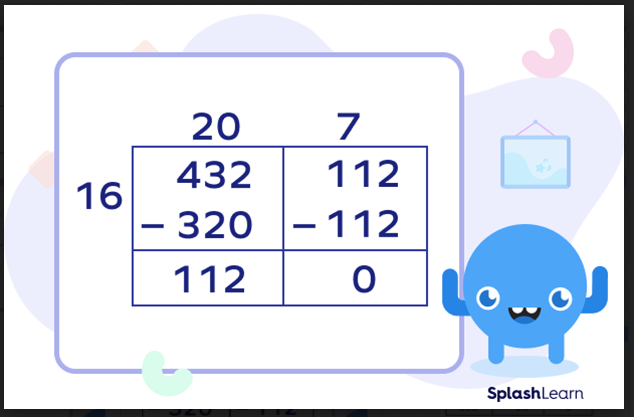
We get the answer: 432 ÷ 16 = 20 + 7 = 27
Another example of area model of division is given below:
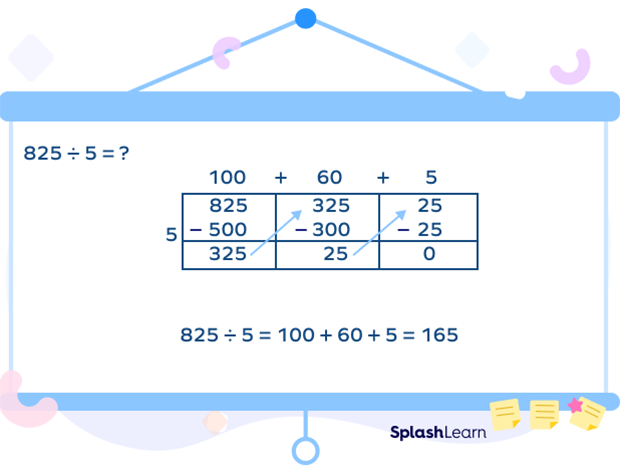
Facts about Area Model
- The area model is also known as the box model.
- This model of multiplication uses the distributive law of multiplication.
- Expanded forms are used to multiply numbers with more than 1 digit.
Solved Examples on Area Model
1. What fraction is given in the figure?
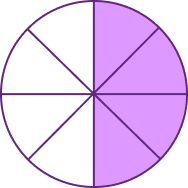
Solution: The denominator is 8. The numerator is 4.
So, the fraction is 48=12.
2. Calculate the product of 48 and 6 by area model.
Solution:
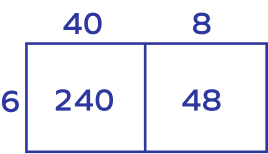
48 × 6 = 240 + 48 = 288
3. Find the product of 39 and 42 using the area model.
Solution:
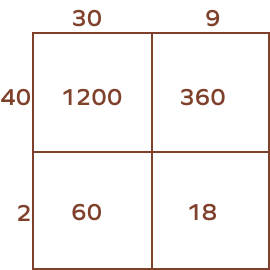
39 × 42 = 1200 + 360 + 60 + 18 = 1638
4. Divide 5607 by 5 using the area model and write the quotient and remainder.
Solution:

Quotient = 1000 + 100 + 20 = 1120 and remainder = 2
5. Multiply $\frac{3}{5}$ and $\frac{2}{3}$ using an area model.
Solution:
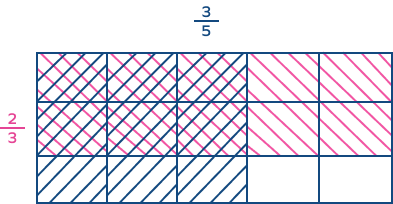
Total mutual shaded parts = 6
Total equal parts = 15
Fraction $= \frac{6}{15} = \frac{2}{5}$
Practice Problems on Area Model
Area Model Multiplication - Definition With Examples
Which of the following model is not the correct representation of the fraction $\frac{3}{5}$?
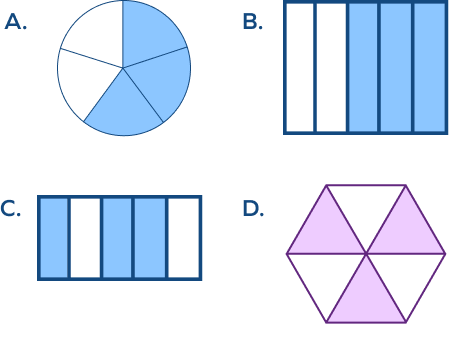
To represent $\frac{3}{5}$, we shade 3 parts out of 5 equal parts.
What will be the value of the blank in the given model for division to find $4870 \div 79$ ?
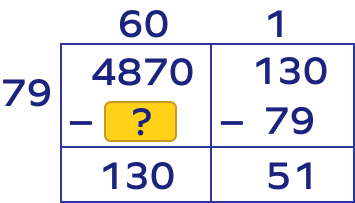
79 × 60 = 4740
What will be the missing number when we multiply 2.3 and 4.7?
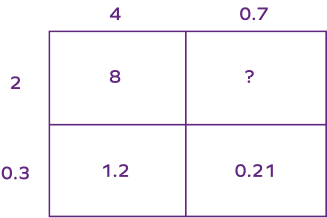
We know 2 × 0.7 = 1.4
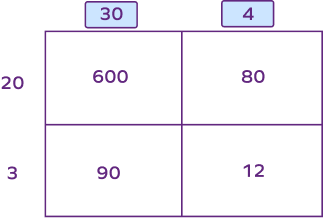
What will be the missing multiplicands in the following model of multiplication?
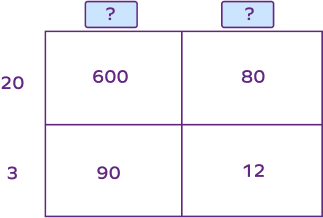
30, 4
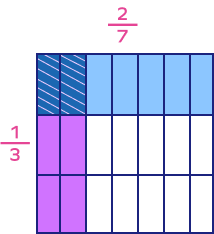
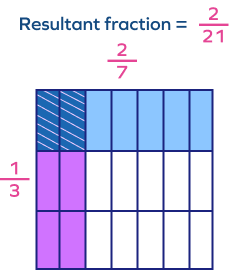
What would be the resultant fraction when two fractions are multiplied using the given model?
$\frac{2}{21}$
Frequently Asked Questions on Area Model
What is the difference between area model and set model of fractions?
In the area model, we divide the whole rectangle—all of its area in equal parts, each with the same area. In the set model, the focus is on the number of objects rather than the area.
What operations can be done on fractions using the area model?
What is the use of the area model of multiplication?
The area model helps the students to understand how math works. The most important use of this model is to visually differentiate between addition and multiplication and demonstrate how distributive property uses both addition and multiplication.
Can we use an area model to multiply polynomial expressions?
Yes, we can use the area model to multiply polynomial expressions. Let’s look at the example given below. Here we are multiplying (x + 2) and (x + 4).
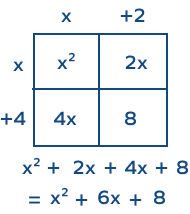
What are partial products in an area model of multiplication?
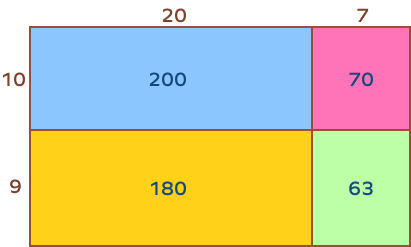
Partial products are the resultant numbers when we multiply each digit of a number to each digit of another number, where every digit also maintains their place value. In the area model of multiplication, the numbers in all the cells, which when added, gives the final product, are known as partial products.
In the given example, when we multiply 19 and 27, we get 200, 180, 70 and 63 as the partial products.